How do you work out retained earnings?
What has retained earnings?
Usually calculated at the end of each financial year by doing the profit and loss account and then deducting any dividends paid out. Then the balance carried forward to the following year and showed in the balance sheet.
Tips for calculating your retained earnings
Take your beginning balance, add your net income, and subtract any dividends paid, and you will have your retained earnings for the year.
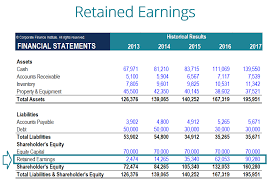
When constituting the balance at the end of each financial year, retained earnings are reported on the balance sheet as the accumulated income from the previous year. That includes the current year’s gain or loss and dividends to the shareholders deducted from the total.
The balance shows the retained earnings on its liability side at the end of the accounting period. That amount represents the accumulated net earnings made by a company from its start, which can be a positive or negative number.
The amount of retained earnings in the report indicates the business’s profitability and can attract investors.
At the end of each period, they calculate the retained earnings in the company.
Usually, make the best use of these funds for working capital and fixed assets for the company or used to pay the company’s debts.
Reporting the Retained Earnings on the balance sheet under the shareholder’s equity section at the end of each accounting period also maintains a summary report called a statement of retained earnings. To outline the changes in RE for a specific period is a usual process in accounting.
The Purpose of Retained Earnings
There are various purposes for retaining, including buying new equipment and machines, spending on research and development, or other activities to increase the company’s growth. This reinvestment into the company aims to achieve even more earnings in the future.
Suppose a company does not believe it can earn a sufficient return on investment from those retained earnings (i.e., make more than its cost of capital). In that case, they often distribute those earnings to shareholders as dividends or conduct share buybacks.
What is the Retained Earnings Formula?
The RE formula is as follows:
RE = Beginning Period RE + Net Income/Loss – Cash Dividends – Stock Dividends
The RE balance may not always be positive, as it may reflect that the current period’s net loss is greater than that of the RE beginning balance. Alternatively, a large distribution of dividends that exceeds the retained earnings balance can cause it to go negative.
How will the changes in net income affect the retained earnings?
How Net Income Impacts Retained Earnings
Factors such as an increase or decrease in net income and incurrence of net loss will pave the way to either business profitability or deficit. The Retained Earnings account can be harmful due to significant, cumulative net losses.
These items include sales revenue, cost of goods sold, depreciation, and other operating expenses. Non-cash items such as write-downs, impairments, and stock-based compensation also affect the account.